
| Use this link to download a full correlation showing how the materials and
activities in Mathematics for College Technology 12 fully meet the Ontario
curriculum.
|
| Click below for the Mathematics for College Technology 12 Final
Exam Final Exam in PDF format Final Exam in Word format |
| Stenhouse Publishers | ||
| Stenhouse Publishers provides professional development books and videos for
teachers. Check out the website for interesting tips, videos, and
articles! ( http://www.stenhouse.com/html/home.htm ) |
||
| http://resources.elearningontario.ca | ||
| Instructions on how to access 3-D Grapher software. ( http://resources.elearningontario.ca ) |
||
| TI-Nspire | ||
| Link to website for the TI-Nspire™ CAS graphing calculator. ( http://www.ti-nspire.com/tools/nspire/index.html ) |
||
| TI-Nspire | ||
| List of shortcut keypad sequences for the TI-Nspire™ CAS graphing
calculator. ( http://education.ti.com/studentzone/product/tips_basics/hotKeys.html ) |
||
| Click here to access The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 11 and 12: Mathematics, 2007 (revised). You will need to scroll down the page to find the correct files, in both PDF Format and Plain Text Format. This document provides the wording for the most recent Ontario curriculum. |
| It is important for students to develop basic math skills in order to have a
solid foundation for their math education. Such skills as recognizing math
symbols, using estimation, and understanding calculator keys are the
stepping stones to achieving success in math. The following blackline masters are designed to help students develop their math skills and understanding. Each blackline master contains exercises that students can complete on their own and/or in small groups. In addition, these handouts can be used to initiate classroom discussion on a number of topics. Encourage your students to complete each blackline master in a separate section of their notebooks for review throughout the term as needed. Math Skills BLMs in Word Format Math Skills BLMs in PDF Format |
| Concern regarding student mathematics achievement has been a focus of
discussion among secondary school teachers and college faculty for some
time. A major outcome of these discussions was the development and
implementation of the College Mathematics Project (CMP). It began as an
investigation into mathematics achievement in applied science and
engineering technology programs at one Ontario college and has grown to
encompass all college programs, with and without mathematics in all Ontario
college programs. The project began in 2004. It is led by Seneca College and
is based at the York Seneca Institute for Mathematics, Science and
Technology Education (YSIMSTE), and has funding to 2011 by the Ministry of
Education (MEd) and the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities
(MTCU).
CMP purpose: The College Mathematics Project uses the methodology of deliberative inquiry to build on the principles of research and deliberation. Its goals are twofold:
CMP Steering Committee membership: The CMP Steering Committee is represented by the Community Colleges Vice President Academics, the Heads of Technology (HOT), the Heads of Business (HOB), the Committee of Registrars, Admissions and Liaison Officers, Colleges Ontario, the Ontario Colleges Mathematics Association, the Ontario Association of Mathematics Educators, the Ontario Mathematics Coordinators Association, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities, secondary and college guidance counsellors, principals, and superintendents. Regional forums are held annually and are organized by the School/College/Work Initiative Regional Planning teams around the province. Research results: The CMP research identifies the importance of secondary school course selection and sequence (pathways) and achievement to success in college mathematics. More recently, the research also suggests that students should apply basic numeracy skills when solving problems requiring higher levels of thinking; in addition, students would benefit from utilizing effective mathematics study skills daily and specific strategies for note-taking, studying, and test-taking. McGraw-Hill-Ryerson considered these recommendations when developing the Study Skills BLMs and Math Skills BLMs for the Online Learning Centre for teachers and students (see the links below). For further information about the research outcomes, teachers can contact their school boards or go to the CMP web site: http://collegemathproject.senecac.on.ca. An invitation to teachers: A key component of the project is to provide an opportunity for secondary and college mathematics educators, counsellors, and administrators to deliberate the research results and share best or promising classroom practices through the regional forums. Outcomes of the forums are reported on the project web site. All secondary and college teachers are encouraged to view these reports. In addition to these reports, there are numerous resources for teachers to utilize. In subsequent years, colleges and school boards may use the CMP data to evaluate the efficacy of interventions and strategies that have been implemented to support student learning. The CMP team welcomes teaching teams to attend the regional forums and to present promising practices being conducted to support mathematics teaching and learning. In a recent CMP summary, project leaders noted that "forums involving multiple colleges are richer in terms of sharing promising practices, improving the understanding and appreciation of the individuality of each college."2 Teachers are encouraged to contact their mathematics coordinator at their respective school board to learn about the CMP research results, how these results can be applied to their teaching practices, discuss how they may become involved in sharing these practices, and learn more about their school’s results. Study Skills BLMs Math SKills BLMs 1Orpwood, G., Schollen, L., Marinelli-Henriques, P., Assiri, H. (2010). College Mathematics Project 2009 Final Report Executive Summary, Toronto, ON: Seneca College of Applied Arts and Technology. 2College Mathematics Project Update for HOT/HOM/HOB, May 2010. |
| Students who consistently apply study skills learn mathematics more
effectively, more productively, and with greater confidence. It is important
for students to learn and apply these study skills early in their academic
career. The following blackline masters are designed to help students develop effective study habits, specifically in the area of mathematics. Each blackline master contains activities that students can complete on their own and/or in small groups. In addition, these handouts can be used to initiate classroom discussion on a number of topics related to study skills (note taking, dealing with mathematics anxiety, organizing study time, and preparing for tests and exams), thereby exposing students to a range of perspectives. Your students’ success in mathematics depends on consistent application of these skills. Encourage your students to complete each activity in a separate section of their notebooks in order to review them throughout the term as needed. Study Skills BLMs in Word Format Study Skills BLMs in PDF Format |
|
Technology Masters in PDF format Extra Technology Masters in PDF format Technology Masters in Word format Extra Technology Masters in Word format |
|
These lessons provided by Texas Instruments
will focus on introducing you to the TI-83 Plus and TI-84 Plus through
various guided interactive activities.
These lessons are provided through Texas Instruments, and as such do
not necessarily follow The Ontario Curriculum, Grades 11 and 12:
Mathematics, 2007 (revised). The following lessons and
activities align with our curriculum and standards and we hope you take
the time to enjoy the module and take from it what you feel will apply
in your classroom setting.
Module 4: Draw on Your Knowledge of
Coordinates Module 5: Transformations Module 8: Solving Equations This module will examine the following: • using the guess-and-test method to solve equations • entering expressions and using concatenation on home screen to solve expressions • entering functions using the y = editor and using the table feature to find missing values • Solving Equations Algebraically store values and compare answers with expressions with rational numbers • using y= editor to graphing and using the Calc menu to find intersection points • expressing answers in fractional form To view these files, Adobe's free Flash Player application is required.
For additional support on this product and material please contact
Texas Instruments.
For more exciting TI-83 Plus and TI-84 Plus modules, please visit the
Texas Instruments site.
http://education.ti.com/educationportal/sites/US/nonProductMulti/pd_onlinealgebra_free.html If you have a TI-Navigator system, please visit the Texas Instruments
site for supporting modules.
http://education.ti.com/educationportal/sites/US/nonProductMulti/pd_onlinemgnavigator_free.html The TI website offers a wide range of free activities for classroom
use. Go to www.education.ti.com and visit the Activities
Exchange portal for more resources that are aligned to Canadian
standards.
* TI-83 Plus and TI-84 Plus are a trademark of Texas Instruments,
Inc.
** TI-Navigator is a trademark of Texas Instruments, Inc. |
|
These lessons provided by Texas Instruments
will focus on introducing you to the TI-Nspire handheld by looking at
the layout of the keypad and the key features of operating the
Applications.
These lessons will focus on introducing you to the TI-Nspire handheld
by looking at the layout of the keypad and the key features of operating
the Applications.
Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 To view these files, Adobe's free Flash Player application is required.
Check out these exciting Texas Instruments web links:
Current TI online TI-NspireTM courses: http://education.ti.com/educationportal/sites/US/sectionHome/tutorials.html Current TI Online courses: http://education.ti.com/educationportal/sites/US/sectionHome/pd_onlinecourses_free.html Current Product Tutorials: http://education.ti.com/educationportal/sites/US/sectionHome/tutorials.html * TI-Nspire is a trademark of Texas Instruments, Inc.
|
| absolute value | The distance from zero to a number on the number line.
|
|||
| algebraic expression | An expression that includes at least one variable. 2t, 3x2 + 4x - 5, and 2x are algebraic expressions. |
|||
| algebraic modelling | The process of representing a relationship by an equation or a
formula, or representing a pattern of numbers by an algebraic
expression. |
|||
| ambiguous case | For a triangle, the case in which two sides and the angle
opposite one of them is given, and there are two distinct solutions. In 
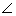


|
|||
| amplitude | Half the difference between the maximum and minimum values of a
periodic function. 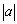
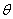
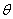
|
|||
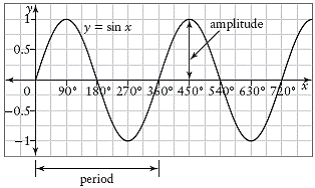
| angle in standard position | The position of an angle when its vertex is at the origin and
its initial arm is on the positive x-axis.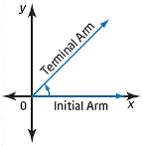
|
|||
| angle of declination | See angle of depression. |
|||
| angle of depression | The angle, measured downward, between the horizontal and the
line of sight from an observer to an object.
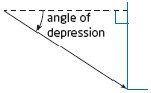
|
|||
| angle of elevation | The angle, measured upward, between the horizontal and the line
of sight from an observer to an object.
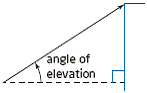
|
|||
| angle of inclination | See angle of elevation. |
|||
| angle of rotation | The measure of degrees that a figure is rotated about a fixed
point. |
|||
| annual rate of interest | The rate at which interest is charged, as a percent, per
year. |
|||
| annuity | A series of equal payments or deposits paid at regular
intervals over a fixed period of time. Common examples of annuities are
mortgages, car payments,
and insurance investments. |
|||
| approximate value | A numerical value that has been rounded. |
|||
| arc | A portion of the circumference of a circle that joins two
points on the circle.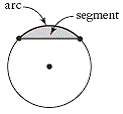
|
|||
| area | The number of square units contained in a two-dimensional
region. |
|||
| associative property |
a + (b + c) = (a + b) +
c for addition and a × (b ×
c) =
(a × b) × c for multiplication. |
|||
| asymptote | A line that a curve approaches more and more closely, but never
touches. This graph has a vertical asymptote at x = –1 and a horizontal asymptote at y = 0. 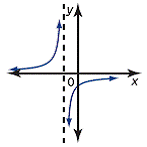
|
|||
| base (of a power) | The number used as a factor for repeated multiplication. In 63, the base is 6. |
|||
| bearing | See true bearing. |
|||
| binomial | A polynomial with two terms. 3x + 4 is a binomial. |
|||
| binomial common factor | See factor by grouping. |
|||
| bisect | To divide into two equal parts. |
|||
| central angle | An angle formed by two radii of a circle. The vertex of the
angle is at the centre of the circle, and the endpoints are on the
circle.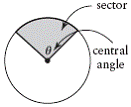
|
|||
| chord (of a circle) | A line segment inside a circle that joins two points on the
circumference of the circle.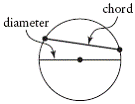
|
|||
| circle | The set of all points in the plane that are equidistant from a
fixed point called the centre. |
|||
| circumference | The distance around a circle. |
|||
| clinometer | An instrument used to measure the angle of elevation or
depression. |
|||
| coefficient | The factor by which a variable is multiplied. In the term 8y, the coefficient is 8; in the term ax, the coefficient is a. |
|||
| common factor | Any factor that two or more numbers, or two or more terms of a
polynomial, share. 2 is a common factor of 4, 6, and 18. 3x is a common factor of 3x2 - 12x. |
|||
| common logarithm | A logarithm in base 10. |
|||
| commutative property |
a + b = b + a for addition and
ab = ba for multiplication. |
|||
| component figure | A simple plane figure that is part of a composite figure. |
|||
| composite figure | A figure made up of two or more simple plane figures. |
|||
| compound interest | Interest paid on the principal and its accumulated
interest. |
|||
| compounding period | The time interval after which compound interest is
calculated. |
|||
| compression | A transformation that is a stretch by a factor greater than 0
and less than 1. |
|||
| congruent | Having the same size and shape. |
|||
| constant function | A function of the form f(x) = c, where
c is any real number. |
|||
| constant term | A term that does not include a variable. In x2 + 5x – 1, the constant term is –1. |
|||
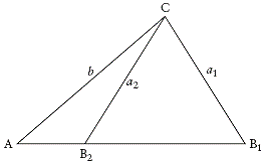
| contained angle | An angle that is formed by two adjacent sides of a
triangle. In the diagram, 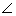
|
|||
| coordinates | The numbers in an ordered pair that locate a point on a
coordinate grid. |
|||
| coordinate grid | A one-to-one pairing of all ordered pairs of real numbers with
all points of a plane. Also called the Cartesian coordinate plane. |
|||
| cosine function | A function of the form y = cos x. The base
function has an amplitude of 1 and a period of 360°.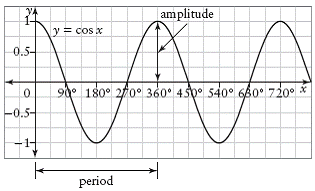
|
|||
| cosine law | The relationship between the lengths of the three sides and the
cosine of an angle in any triangle.
|
|||
| cosine ratio | In a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the adjacent
side to the length of the hypotenuse.
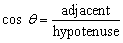
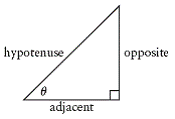
|
|||
| cube root | Given a number a, the number b such that
b3 = a.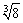
|
|||
| cubic function | A polynomial function of degree 3. |
|||
| cycle | One complete pattern of a periodic function. |
|||
| cyclic quadrilateral | A quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. |
|||
| cylinder | A solid figure with two identical flat circular ends and one
curved side. |
|||
| decibel scale | A logarithmic scale used to compare sound levels. |
|||
| decomposition (factoring by) | A method used to factor quadratic polynomial expressions that
involves writing a polynomial as a composition of simpler polynomials. 6x2 – 5x + 1 = 6x2 – 2x – 3x + 1 Rewrite the middle term as the sum of two terms. = (6x2 – 2x) + (–3x + 1) Then, factor by grouping. = 2x(3x – 1) – 1(3x – 1) = (3x – 1)(2x – 1) |
|||
| degree of a polynomial | The greatest exponent of the variable in any one term. The degree of x3 + 6x2 - 1 is 3. |
|||
| diagonal | A line segment joining two non-adjacent vertices of a
polygon. |
|||
| diameter | A chord that passes through the centre of a circle. Diameter =
2 × radius. |
|||
| difference of squares | An expression of the form a2 –
b2 that involves the subtraction of two
squares. x2 – 25 is a difference of squares. |
|||
| dimension | A measurement such as length, width, or height. |
|||
| directed line segment | A line segment with a specified direction that is indicated by
an arrowhead; a vector. |
|||
| direction of a vector | An angle of rotation of a vector about its tail. It can be
expressed as either a true bearing (bearing) or as a quadrant bearing. |
|||
| displacement (of an object) | The distance along a straight line from an initial point to a
final point. |
|||
| displacement (of a vector) | A vector quantity describing the position of an object. |
|||
| distributive property | The property that a(b + c) =
ab + ac when a, b, and c are
real
numbers. It is used to expand, or multiply, polynomial expressions. |
|||
| domain | The set of all values of the first coordinates of the ordered
pairs, or the independent variable, in a relation. |
|||
| end behaviour | The behaviour of the y-values of the function as
x approaches
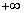
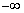
|
|||
| equidistant | The same distance apart at every point. |
|||
| equivalent vectors | Vectors that have the same magnitude and direction. |
|||
| even-degree function | A function in which the term with the highest degree has an
even degree. |
|||
| even-degree polynomial | A polynomial in which the term with the highest degree has an
even degree. |
|||
| even function | A function f(x) that satisfies the property
f(–x) = f(x) for all x in
its domain. An
even function is symmetric about the y-axis.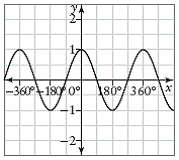
|
|||
| even order | See zero of even order. |
|||
| exact value | A precise value in which accuracy is preserved. Rounded decimal
answers are approximate values, while fractions are exact values. |
|||
| expand | To write a quantity as a sum of terms in extended form. To
multiply (usually applied to polynomials). 4(n - 3) expands to 4n - 12. |
|||
| exponent | The raised number that denotes repeated multiplication of a
base. In 3x4, the exponent is 4. |
|||
| exponent laws | Rules used for expressions involving powers. |
|||
| exponential decay | A pattern of decay in which each term is multiplied by a
constant amount, between 0 and 1, to produce the next term. |
|||
| exponential equation | An equation that has a variable in an exponent. 3x = 81 is an exponential equation. |
|||
| exponential function | A function in which a variable is an exponent. It can be
defined by an equation of the form y = abx,
where
a ≠ 0, b > 0, and b ≠ 1. |
|||
| exponential growth | A pattern of growth in which each term is multiplied by a
constant amount, greater than 1, to produce the next term. |
|||
| factor | To express a number as the product of two or more numbers, or
an algebraic expression as the product of two or more other algebraic
expressions. Also, the
individual numbers or algebraic expressions in such a product. |
|||
| factor by grouping | A method of factoring by which groups of two terms are common
factored to produce a binomial common factor. bx + 3x + by + 3y = (bx + 3x) + (by + 3y) Group sets of two terms. = x(b + 3) + y(b + 3) Common factor each group. = (b + 3)(x + y) Common factor again, using the binomial common factor. |
|||
| finite differences | Differences between the y-values in a table of values
with evenly spaced
x-values. See first differences and second
differences. |
|||
| first differences | Differences between consecutive y-values in a table of
values with evenly spaced x-values.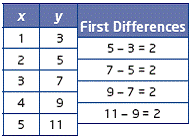
|
|||
| force | A vector quantity that describes an influence that can cause an
object of a given mass to move in a certain direction. |
|||
| function | A relation between two variables, such as x and
y, in which each value of x is mapped onto exactly one
value of y. |
|||
| function notation | A notation that describes a function. It denotes that for a
function f, when x is a value in the
domain, f(x) represents the corresponding value in the range. f(x) =x + 4 is a linear function expressed using function notation. |
|||
| graphing calculator | A handheld device capable of a wide range of mathematical
operations, including graphing from an equation, constructing a scatter
plot,
determining the equation of a line of best fit for a scatter plot, making
statistical calculations, and performing elementary symbolic manipulation.
Many graphing
calculators will attach to scientific probes that can be used to gather data
involving physical measurements, such as position, temperature, and
force. |
|||
| greatest common factor (GCF) | The greatest number and/or variable that is a factor of each
term in a polynomial expression. The GCF of 12ab and 8bc is 4b. |
|||
| ground velocity | The velocity of an object relative to the ground. Also called
the bearing velocity, it is the resultant when the air velocity and the
effect of wind or current are added. |
|||
| half-life | The length of time for an unstable element to spontaneously
decay to one half of its original amount. |
|||
| head of a vector | The tip or arrowhead of a vector. |
|||
| heading | The direction in which a vessel is pointed in order to overcome
other forces, such as wind or current, with the intended resultant direction
being the bearing. |
|||
| head-to-tail method for adding vectors | A method of adding two vectors.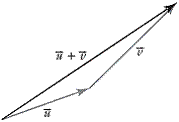
|
|||
| hemisphere | Half of a sphere (ball). |
|||
| hexagon | A polygon with six sides. |
|||
| horizontal asymptote | A horizontal line that a curve approaches more and more
closely, but never touches. This graph has a horizontal asymptote at y = 0. 
|
|||
| horizontal component (of a vector) | A horizontal vector, which when added to a vertical
vector gives the resultant vector. |
|||
| horizontal compression |
|
|||
| horizontal displacement (of an object) | The horizontal distance an object has moved from an initial
point to a final point. |
|||
| horizontal stretch |
|
|||
| horizontal translation (or shift) | A transformation where (x, y) on
the graph of y = f(x) is transformed to (x +
h, y) on the graph of y = f(x - h). |
|||
| hypotenuse | The longest side of a right triangle. |
|||
| identity property of addition | The property that states that the sum of any number or variable
and zero is the number or variable itself. a + 0= a = 0 + a |
|||
| identity property of multiplication | The property that states that the product of any number or
variable and one is the number or variable itself. a ×1 = a = 1 × a |
|||
| imperial system | A collection of units that includes inches, feet, and miles for
length; cups, quarts, and gallons for volume; and ounces and pounds for
weight. |
|||
| initial arm | The arm of an angle in standard position that is on the
positive x-axis.
|
|||
| inscribed angle | An angle in a circle with its vertex on the circle.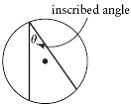
|
|||
| integer | The set of whole numbers and their opposites, represented by
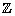
... –3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ... |
|||
| intercept | The distance from the origin of the xy-plane to the
point at which a line or curve crosses a given axis. |
|||
| interest rate | The percent of the principal that is earned, or paid, as
interest. |
|||
| International system of units (SI) | The internationally recognized standard metric system. See
metric system. |
|||
| interval of increase/decrease | The x-values by which a function is
increasing/decreasing. |
|||
| inverse of a function | A function that undoes another function. For function
f and its inverse f–1, if f
(a) =
b, then f–1(b) = a. The inverse of y= bx is x= by, which can be written as y = logb x. 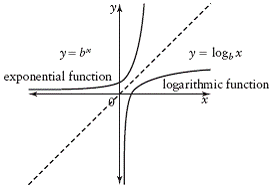
|
|||
| inverted | Upside down. |
|||
| isosceles trapezoid | A trapezoid with equal non-parallel sides and equal base
angles. |
|||
| isosceles triangle | A triangle with exactly two equal sides. |
|||
| leading coefficient | The coefficient of the greatest power of x in a
polynomial P(x). |
|||
| like terms | Terms that have exactly the same variable(s) raised to exactly
the same exponent(s). 3x2, –x2, and 2.5 x2 are like terms. |
|||
| line symmetry | A graph has line symmetry if there is a line x = a
that divides the graph into two parts such that each part is a reflection of
the other
in the line x = a. |
|||
| linear function | A function of the form f(x) = mx +
b, where m and b are constants. |
|||
| linear relation | A relation between two variables that appears as a straight
line when graphed on a coordinate system. May also be referred to as a
linear function. |
|||
| local maximum | A point on a function that has the greatest y-value on
some interval close to the point. |
|||
| local minimum | A point on a function that has the least y-value on
some interval close to the point. |
|||
| logarithm | The logarithm of a number is the value of the exponent to which
a given base must be raised to produce the given number. log3 81 = 4, because 34 = 81. |
|||
| logarithmic equation | An equation that has the variable in a logarithm. log2x = log2 3 + log2 5 is a logarithmic equation. |
|||
| logarithmic function | The inverse of an exponential function. A function of the form
f(x) = logb x, where
b > 0 and b ≠ 1. See inverse of a
function. y = logb x can be written as by = x. |
|||
| logarithmic scale | A scale that uses powers of 10, such as the decibel scale. |
|||
| magnitude (of a vector) | The length of the directed line segment. It is designated using
absolute value brackets, so the magnitude of vector
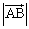
|
|||
| mapping diagram | A graphical representation that relates the values in one set,
the domain, to a second set, the range, using directed arrows from domain to
range.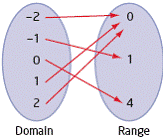
|
|||
| mass | A measurement of the quantity of matter in an object, measured
in such units as milligrams, grams, kilograms, or tonnes. |
|||
| mathematical model | A mathematical description of a real situation. The description
may include a diagram, a graph, a table of values, an equation, a formula, a
physical model, or a computer model. |
|||
| mathematical modelling | The process of describing a real situation in mathematical
form. |
|||
| maximum point | A local maximum point in a function. See local
maximum. |
|||
| maximum value | The y-value of the maximum point. |
|||
| method of decomposition | See decomposition (factoring by). |
|||
| metric system | A collection of units that includes centimetres, metres, and
kilometres for length; millilitres and litres for volume; and grams and
kilograms for weight. |
|||
| midpoint | A point equidistant from the ends of a line segment. |
|||
| minimum point | A local minimum point in a function. See local
minimum. |
|||
| minimum value | The y-value of the minimum point. |
|||
| momentum | A measure of the motion of a body. |
|||
| monomial | An algebraic expression with one term. 7x is a monomial. |
|||
| net | A two-dimensional diagram that shows a three-dimensional object
"unfolded" so that all of its faces are visible. This is a net for a
triangular prism.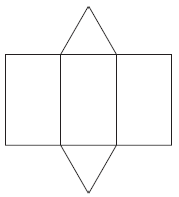
|
|||
| nth root | A root where the index is the variable n. Given a
number a, the number b such that bn=
a. |
|||
| oblique triangle | A triangle that is not right-angled. |
|||
| obtuse angle | An angle that measures more than 90°, but less than
180°. |
|||
| obtuse triangle | A triangle containing one obtuse angle. |
|||
| octagon | A polygon with eight sides. |
|||
| odd-degree function | A function in which the term with the highest degree has an odd
degree. |
|||
| odd-degree polynomial | A polynomial in which the term with the highest degree has an
odd degree. |
|||
| odd function | A function that satisfies the property
f(–x) = –f(x) for all
x in its domain. An odd function is
symmetric about the origin.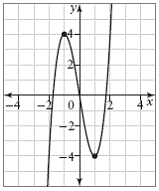
|
|||
| odd order | See zero of odd order. |
|||
| opposite angle (of a triangle) | The angle directly across from a given side of a triangle. |
|||
| opposite vectors | Vectors that have the same magnitude but opposite direction;
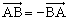
|
|||
| order (of a zero) | If a polynomial function has a factor (x –
a) that is repeated n times, then x = a
is a zero of order n.
The function f(x) = 2(x + 1)2 has a zero of order 2. |
|||
| ordered pair | A pair of numbers, such as (3, 8), used to locate a point on a
graph. |
|||
| origin | The point of intersection of the x-axis and the
y-axis on a coordinate grid. The point (0,0) is the origin. |
|||
| parallelogram | A quadrilateral whose opposite sides are both parallel and
equal in length. |
|||
| parallelogram method for adding vectors | A method for adding two vectors.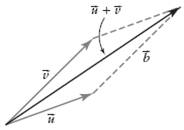
|
|||
| parameter | A constant that can vary but does not change the form of the
expression or equation. In the equation f(x) = a sin [k(x – d)] + c, the parameters are a, k, d, and c. |
|||
| perfect square trinomial | The trinomial that results from squaring a binomial. |
|||
| perimeter | The distance around a polygon. |
|||
| period | The magnitude of the interval of the domain over which a
periodic function repeats itself. The horizontal length of one
cycle.
|
|||
| periodic function | A function that repeats itself over regular intervals of its
domain. Its graph has a wave-like appearance. f(x) = sin x and f(x) = cos x are periodic functions. |
|||
| periodic phenomenon | A real-world situation that can be modelled with a periodic
function, such as a heartbeat. |
|||
| perpendicular | At a 90° angle to. |
|||
| perpendicular components (of a vector) | The vertical and horizontal vectors whose sum gives a resultant
vector. |
|||
| pH scale | A logarithmic scale used to measure how acidic or alkaline a
substance is. Defined as pH = –log [H+], where
[H+]
is the concentration of hydronium ions, in moles per litre. |
|||
| phase shift | The horizontal translation of a trigonometric function. |
|||
| Platonic solid | A polyhedron with every face being a regular polygon of the
same size and shape. |
|||
| point of tangency (to a circle) | The point where a tangent line touches a circle. |
|||
| point symmetry | A graph has point symmetry about a point (a,
b) if each part of the graph on one side of (a,
b) can be rotated
180° to coincide with part of the graph on the other side of (a,
b). |
|||
| polynomial expression | An algebraic expression formed by adding or subtracting one or
more terms that are the product of a constant and a power of x with
a whole number as an exponent. |
|||
| polynomial function | A polynomial function of the form P(x) =
anxn + ... +
a2x2 +
a1x + a0, where n is a
positive integer. |
|||
| power | An abbreviation indicating how many times a number, symbol, or
expression is multiplied by itself. 53, x6, (y + 3)2, and am are powers. |
|||
| primary data | Data gathered by performing an experiment or by conducting an
observational study. |
|||
| primary trigonometric ratios | The sine ratio, cosine ratio, and tangent ratio, defined in
right triangles.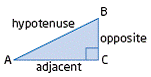
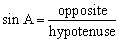
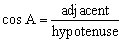
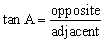
|
|||
| principal | An amount of money invested or borrowed. |
|||
| product | The result of multiplication. |
|||
| pyramid | A polyhedron with one base in the shape of a polygon and the
same number of lateral triangular faces as there are sides in the base. |
|||
| Pythagorean theorem | In a right triangle, the square of the length of the longest
side is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two
sides.
|
|||
| quadrant | One of the four regions formed by the intersection of the
x-axis and the y-axis.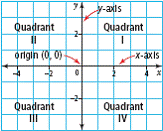
|
|||
| quadrant bearing | A compass measurement between 0° and 90° east or west
of the north–south line. See true bearing. |
|||
| quadratic function | A function defined by a quadratic equation. In standard form: y = ax2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c 
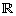
In factored form: y = a(x – r)(x – s), where a ≠ 0, and r and s 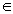
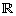
In vertex form: y = a(x – h)2 + k, where a ≠ 0 and the vertex is at (h, k). |
|||
| quarterly | Four times per year; every three months. |
|||
| quartic function | A polynomial of degree four. |
|||
| radius | The length of a line segment extending from the centre to the
circumference of the circle. |
|||
| range of a function or relation | The set of all second coordinates of the ordered
pairs of a relation. |
|||
| range of a set of numbers | The difference between the greatest and least values in a set
of data. |
|||
| rate of increase/decrease | The steepness or slope of a function. The ratio of the change
in the output value and the change in the input value of a function. |
|||
| ratio | A comparison of quantities with the same unit. |
|||
| rational number | A number that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers,
where the divisor is not zero. 0.75, 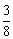
|
|||
| real number | A member of the set of all rational and irrational numbers,
represented by
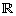
|
|||
| rectangular components of a vector | The vertical and horizontal vectors whose sum gives a resultant
vector. |
|||
| rectangular prism | A three-dimensional figure with six rectangular faces. |
|||
| reference angle | The acute angle between the terminal arm and the
x-axis. |
|||
| reflection | A transformation in which a point or figure is reflected in a
line of reflection.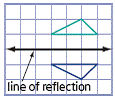
|
|||
| related angle | The acute angle with a trigonometric function having the same
absolute value as a given angle outside the first quadrant. |
|||
| relation | An identified pattern between two variables that may be
expressed as ordered pairs, a table of values, a graph, or an equation. |
|||
| resolution of a vector | The act of resolving a vector into its two perpendicular, or
rectangular, vector components (one vertical and one horizontal) whose sum
is the given vector. |
|||
| restriction | A constraint on the value(s) of a variable. In 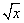
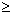
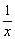
|
|||
| resultant force | The sum of two or more forces. |
|||
| resultant vector | The sum or difference of two or more vectors. |
|||
| rhombus | A parallelogram in which the lengths of all four sides are
equal.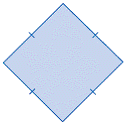
|
|||
| Richter scale | A logarithmic scale used to measure the magnitude of
earthquakes. |
|||
| right angle | An angle that measures 90°. |
|||
| right bisector of a line segment | A line that is perpendicular to a line segment and divides the
line segment into two equal parts. |
|||
| right triangle | A triangle containing a 90° angle. |
|||
| roots | The solutions of an equation. |
|||
| rotation angle | See angle of rotation. |
|||
| scalar | A quantity that has magnitude but no direction, such as time,
temperature, or volume. |
|||
| secant to a circle | A line that intersects a circle at two distinct points.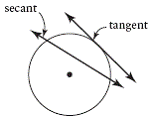
|
|||
| second differences | Differences between consecutive first differences in a table of
values with evenly spaced x-values.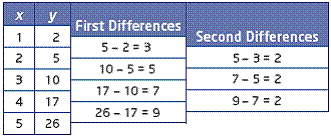
|
|||
| secondary data | Data collected by someone else. |
|||
| sector | A part of a circle bounded by two radii and an arc of the
circle.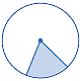
|
|||
| segment of a circle | A part of a circle bounded by a chord and an arc of the
circle.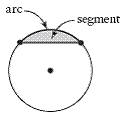
|
|||
| semi-annually | Two times per year; every six months. |
|||
| sine function | A function of the form y = sin x. The base
function has an amplitude of 1 and a period of 360°.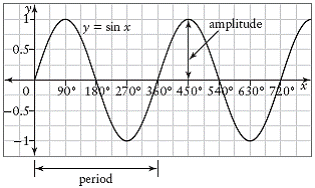
|
|||
| sine law | The relationship between the lengths of the sides and their
opposite angles in any triangle.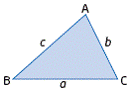
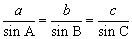
|
|||
| sine ratio | In a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the opposite
side to the length of the hypotenuse.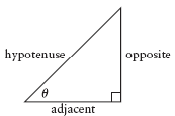
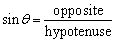
|
|||
| sinusoidal function | A function with the curved form of a sine wave that is used to
model periodic data.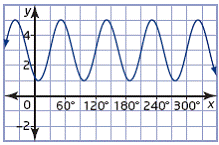
|
|||
| slant height | The length of a slanted side or slanted edge, such as the
slanted side of a cone or slanted edge of a pyramid. |
|||
| solve a triangle | Determine the measures of all angles and the lengths of all
sides of a triangle. |
|||
| special angles | Angles for which exact trigonometric ratios can be found:
30°, 45°, 60°, 90° and their related angles in quadrants II,
III, and IV. |
|||
| special triangles | Triangles used to find the exact trigonometric ratios for
30°, 45°, 60° and their related angles in quadrants II, III and
IV.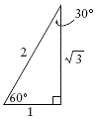
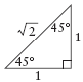
|
|||
| sphere | A three-dimensional figure shaped like a ball. |
|||
| stretch | A transformation that results in the distance from the
x-axis of every point growing by a scale factor greater than 1
(vertical stretch) or the
distance from the y-axis of every point growing by a scale factor
greater than 1 (horizontal stretch). |
|||
| subtend | Lie opposite to. An arc or a chord can subtend an angle at the
centre or at the circumference of a circle. The arc, AB, of the circle shown subtends 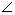
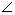
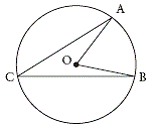
|
|||
| surface area | The area of the surfaces of a three-dimensional figure. |
|||
| symmetry | A quality of a plane figure so that it can be folded along a
fold line and the halves of the figure match exactly. |
|||
| tail of a vector | The origin or starting point of a vector. |
|||
| tangent ratio | In a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the opposite
side to the length of the adjacent side.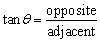

|
|||
| tangent to a circle | A line that touches the circle at exactly one point and equals
the slope of the curve at that point.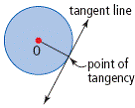
|
|||
| tension | The measure of a force that is stretching or pulling an
object. |
|||
| terminal arm | The arm of an angle in standard position that is not on the
positive x-axis.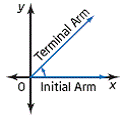
|
|||
| transformation | A change made to a figure or a relation such that the figure or
the graph of the relation is shifted or changed in shape. |
|||
| translation | A slide transformation that results in a shift of the original
figure without changing its shape. |
|||
| trapezoid | A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.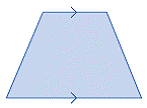
|
|||
| triangle method for adding vectors | See head-to-tail method for adding vectors. |
|||
| triangular prism | A prism with triangular bases.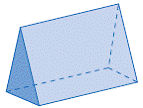
|
|||
| trigonometric function | A function involving a trigonometric ratio. y = 3 cos (x + 2) – 4 is a trigonometric function. |
|||
| trigonometric ratios | See primary trigonometric ratios. |
|||
| true bearing | An angle of rotation measured clockwise from north and
expressed as a three-digit number. Also called azimuth bearing.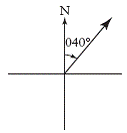
|
|||
| unit circle | A circle of radius 1 unit that is centred at the origin. |
|||
| variable | A letter or symbol, such as x, used to represent an
unspecified number. x and y are variables in the expression 2x + 3y. |
|||
| vector | A quantity that has both magnitude and direction, such as
displacement or velocity. |
|||
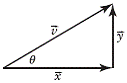
| vector components | The perpendicular components, 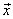
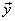
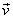
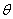
|
|||
| velocity | The rate of change of position of an object; velocity is a
vector quantity. |
|||
| vertex | A point at which two sides of a polygon meet. |
|||
| vertical component (of a vector) | A vertical vector, which when added to a horizontal vector
gives the resultant vector. |
|||
| vertical compression | A transformation where (x, y) on the graph of
y = f(x) is transformed to (x,
ay) on the graph of y = af(x), when 0
< a < 1. |
|||
| vertical displacement (of an object) | The vertical distance an object has moved from an
initial point to a final point. |
|||
| vertical line test | A method of determining whether a relation is a function. If a
vertical line intersects the graph of a relation at exactly one point, then
the
relation is a function. |
|||
| vertical stretch | A transformation where (x, y) on the graph of
y = f(x) is transformed to
(x, ay) on the graph of y =
af(x), when a > 1. |
|||
| vertical translation or shift | A transformation where (x, y) on the graph of
y = f(x) is transformed to (x,
y +k) on the graph of y = f(x) + k. |
|||
| volume | The amount of three-dimensional space an object occupies. |
|||
| whole number | A number in the sequence 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... . |
|||
| x-intercept | The x-coordinate of the point where a line or curve
crosses the x-axis. |
|||
| y-intercept | The y-coordinate of the point where a line or curve
crosses the y-axis. |
|||
| zero of a function | Any value of x for which the value of the function is
zero. It corresponds to the x-intercept(s) of the graph of the
function. |
|||
| zero of even order | An x-intercept that just touches the
x-axis. |
|||
| zero of odd order | An x-intercept that crosses the x-axis. |
|||
| zero vector | A vector with a magnitude of zero. |
|||
| Basic math skills provide a solid foundation for learning. These skills are
necessary in order for you to move forward in your math education. Such
skills as recognizing math symbols, using estimation, and understanding
calculator keys are the stepping stones to achieving success.
The following blackline masters are designed to develop your math skills and understanding. By gaining and practising these skills, you may find that you achieve greater understanding in your math classes and, ultimately, improve your performance on assignments and tests. Complete each blackline master in a separate section of your notebook so that you can review your math skills throughout the term as needed. Math Skills BLMs in Word Format Math Skills BLMs in PDF Format |
| Your success at school depends on your ability to study effectively and
efficiently. No two students study the same way. However, there are some
general study techniques that have been proven to benefit mathematics
learning, reduce mathematics anxiety, and improve test results. When
students don’t make consistent use of proven study techniques,
valuable study time is wasted. The result is frustration and stress, and
possibly poor grades.
The following blackline masters are designed to teach you study skills that, when applied on a daily basis, may improve your learning, understanding, and, ultimately, your marks. Complete each activity in a separate section of your notebook in order to review these study skills throughout the term as needed. Study Skills BLMs in Word Format Study Skills BLMs in PDF Format |
|
Videos in SWF format
NSpirelinestyle How to change the line-style for graphing functions on the N-Spire. ti83linestyleV2 How to change the line-style for graphing functions on the TI83+/84. ti83piecewise How to graph piecewise functions on the TI83+/84. ti83table Setting up a table and table parameters on the TI83+/84. ti83window Setting the viewing window to view functions optimally on the TI83+/84. Zoomtrig Setting the viewing window to view trigonometric functions properly on the TI83+/84. ti83graph How to graph functions on the TI83+/84. ti83intersect How to find the coordinates of intersection of two functions on the TI83+/84. ti83maxmin Finding maxima and minima of functions using the TI83+/84. GSPFunc Plotting functions in the Geometer’s Sketchpad. Videos in WMW format
NSpirelinestyle How to change the line-style for graphing functions on the N-Spire. ti83linestyleV2 How to change the line-style for graphing functions on the TI83+/84. ti83piecewise How to graph piecewise functions on the TI83+/84. ti83table Setting up a table and table parameters on the TI83+/84. ti83window Setting the viewing window to view functions optimally on the TI83+/84. ti83graphV2 How to graph functions on the TI83+/84. Zoomtrig Setting the viewing window to view trigonometric functions properly on the TI83+/84. ti83intersect How to find the coordinates of intersection of two functions on the TI83+/84. ti83maxmin Finding maxima and minima of functions using the TI83+/84. GSPFunc Plotting functions in the Geometer’s Sketchpad. |
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 1.1, p. 2, questions 2 and 3: |
||
| Sine Box | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/products/trig/applets/sinBox/sinBox.html ) |
||
| Cosine Box | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/products/trig/applets/cosbox/cosbox.html ) |
||
| Tanget Box | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/products/trig/applets/tanbox/tanbox.html ) |
||
| Trig Functions | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/products/trig/applets/sixtrigfn/sixtrigfn.html ) |
||
|
Section 1.4, p. 14: |
||
| Platonic Solids: | ||
|
( http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_128_g_4_t_3.html?open=instructions&from=category_g... ) |
||
|
Section 1.5: |
||
| The Law of Sines: | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/seigen/seigen.html ) |
||
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 2.1: |
||
| The graph of y = sin x | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/samples/graphSinX.html ) |
||
| Unit Circle and Trigonometric Functions | ||
|
( http://science.kennesaw.edu/~plaval/tools/trig.html ) |
||
| Generating the Sine Graph | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/sine_gen_80.gif ) |
||
| Generating the Cosine Graph | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/cos_gen_80.gif ) |
||
|
Section 2.2: |
||
| Family of Sine Functions (Translations) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/sine_func_vary_c_80.gif ) |
||
| Family of Sine Functions (Translations) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/sine_func_vary_c_80.gif ) |
||
| Family of Cosine Functions (Translations) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/cosine_func_vary_c_80.gif ) |
||
| Family of Cosine Functions (Translations) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/cosine_func_vary_d_80.gif ) |
||
| Section 2.3: |
||
| Family of Sine Functions (Stretches and Compressions) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/sine_func_vary_a_80.gif ) |
||
| Family of Sine Functions (Stretches and Compressions) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/sine_func_vary_b_80.gif ) |
||
| Family of Cosine Functions (Stretches and Compressions) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/cosine_func_vary_a_80.gif ) |
||
| Family of Cosine Functions (Stretches and Compressions) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/family_of_functions/cosine_func_vary_b_80.gif ) |
||
|
Section 2.4: |
||
| Graphs of Transformations of the Sine and Cosine Functions | ||
|
( http://www.members.shaw.ca/ron.blond/sc.APPLET/index.html ) |
||
| The graph of y = a sin b(x – c) (Transformations) | ||
|
( http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/ABCsinX/ABCsinX.html ) |
||
| Determining the Equation of a Sinusoid (Transformations) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/sinusoidapp/sinusoidpractice.html ) |
||
|
Section 2.6, p. 41, question 5: |
||
| Simple Pendulum | ||
|
( http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph14e/pendulum.htm ) |
||
| Applet: Pendulum | ||
|
( http://www.lon-capa.org/~mmp/kap13/cd363a.htm ) |
||
|
Section 2.6, p. 41, question 6, and p. 42, question
11: |
||
| Sinusoids: Applications and Modeling (Ferris Wheel) | ||
|
( http://mathdemos.gcsu.edu/mathdemos/sinusoidapp/sinusoidapp.html ) |
||
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 3.1 |
||
| Azimuths (Bearings) and Compass Quadrant Bearings | ||
|
( http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/geology/leveson/core/linksa/comp.html ) |
||
|
Section 3.2 |
||
| Vector Arithmetic Java Visualization | ||
|
( http://www.pa.uky.edu/~phy211/VecArith/index.html ) |
||
| Section 3.3 |
||
| Vector Arithmetic Java Visualization | ||
|
( http://www.pa.uky.edu/~phy211/VecArith/index.html ) |
||
| Section 3.4 |
||
| Vector Arithmetic Java Visualization | ||
|
( http://www.pa.uky.edu/~phy211/VecArith/index.html ) |
||
|
Section 3.5, p. 58, question 5, and p. 59, question
13 |
||
| Plane Landing (Effect of Wind Vector) | ||
|
( http://www.break.com/usercontent/2009/7/plane-landing-on-heavy-wind-almost-crashes-883934... ) |
||
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 4.1 |
||
| Law of Exponents | ||
|
( http://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/exponent-laws.html ) |
||
|
Section 4.2 |
||
| The Exponential Function y = ab^x | ||
|
( http://members.shaw.ca/ron.blond/TLE/ExpFcn.APPLET/index.html ) |
||
|
Section 4.3 |
||
| Applications of Exponential Functions | ||
|
( http://www.algebralab.org/lessons/lesson.aspx?file=Algebra_ExponentsApps.xml ) |
||
|
Section 4.6 |
||
| Stellar Magnitude (Problem-Solving With Logarithms) | ||
|
( http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/astr162/lect/stars/magnitudes.html ) |
||
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 5.2 |
||
| Polynomial Function Graphs | ||
|
( http://id.mind.net/~zona/mmts/functionInstitute/polynomialFunctions/graphs/polynomialFunc... ) |
||
|
Section 5.5 |
||
| Application of Polynomials | ||
|
( http://www.mathmotivation.com/science/calculator-functions.html ) |
||
|
Section 5.6 |
||
| Factoring Polynomials with Tiles | ||
|
( http://staff.argyll.epsb.ca/jreed/math9/strand2/2210.htm ) |
||
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 6.1: |
||
| Expression Calculator | ||
|
( http://www.algebrahelp.com/calculators/expression/oops/ ) |
||
|
Section 6.2: |
||
| Factoring Calculator | ||
|
( http://www.algebrahelp.com/calculators/expression/factoring/ ) |
||
| Factoring Calculator | ||
|
( http://www.freemathhelp.com/factoring-calculator.php ) |
||
|
Section 6.4, p. 122, question 5: |
||
| PSI–kPa Pressure Converter | ||
|
( http://www.csgnetwork.com/presskpapsicvt.html ) |
||
|
Section 6.5, p. 126, question 7: |
||
| Home Improvement Costs | ||
|
( http://www.allaroundthehouse.com/lib.repr.htm ) |
||
| Roof Repair Cost | ||
|
( http://www.costhelper.com/cost/home-garden/roof-repair.html ) |
||
| How to Calculate Roof Replacement Costs | ||
|
( http://www.ehow.com/how_4811445_calculate-roof-replacement-costs.html ) |
||
|
Section 6.5, p. 126, question 9: |
||
| Home Improvement Costs | ||
|
( http://www.allaroundthehouse.com/lib.repr.htm ) |
||
| Insulation: The Different Types and Their Advantages and Disadvantages | ||
|
( http://www.aerias.org/DesktopModules/ArticleDetail.aspx?articleId=95 ) |
||
| Building insulation materials | ||
|
( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Building_insulation_materials ) |
||
| Insulating Your House | ||
|
( http://www.cmhc-schl.gc.ca/en/co/maho/enefcosa/enefcosa_002.cfm ) |
||
| Insulation | ||
|
( http://www.homedepot.ca/catalog/insulation/173074 ) |
||
| Insulating materials | ||
|
( http://www.rona.ca/shop/insulating-materials_building-materials-accessories_shop ) |
||
|
Section 6.5, p. 127, question 16: |
||
| Jobs That Use Mathematical Modeling | ||
|
( http://www.xpmath.com/careers/topicsresult.php?subjectID=5&topicID=10 ) |
||
|
Chapter Test in Word Format Chapter Test in PDF Format |
| Want a fun way to test your knowledge of math terms? Try this Crossword Puzzle and see how many you can get! |
|
Section 7.1 |
||
| Metric and Imperial Conversion Charts and Tables | ||
|
( http://convert.french-property.co.uk/ ) |
||
| Metric Conversion – Metric to Imperial Conversion Calculators | ||
|
( http://www.metric-conversion.biz/ ) |
||
| Length conversion – Online length converter | ||
|
( http://www.sciencemadesimple.com/length_conversion.php ) |
||
| Meters to Feet Conversion | ||
|
( http://www.metric-conversions.org/length/meters-to-feet.htm ) |
||
| Conversion tables | ||
|
( http://www.convert-me.com/en/ ) |
||
| Online conversion | ||
|
( http://www.onlineconversion.com/ ) |
||
| Metric Conversion & Metric System | ||
|
( http://www.france-property-and-information.com/metric_conversion_table.htm ) |
||
| Metric Conversion Chart | ||
|
( http://www.sciencemadesimple.com/metric_conversion_chart.html ) |
||
|
Section 7.1, p. 131, question 8 |
||
| Metric Conversion & Metric System | ||
|
( http://www.france-property-and-information.com/metric_conversion_table.htm ) |
||
|
Section 7.1, p. 132, question 11 |
||
| Rolling With Reuleaux (Reauleaux Triangle) | ||
|
( http://www.maa.org/mathland/mathland_10_21.html ) |
||
|
Section 7.1, p. 134, question 25 |
||
| How to Build a Scale House Model | ||
|
( http://www.ehow.com/how_4911345_build-scale-house-model.html ) |
||
|
Section 7.2 |
||
| Surface Area Calculator | ||
|
( http://www.csgnetwork.com/surfareacalc.html ) |
||
|
Section 7.3 |
||
| Metric and Imperial Conversion Charts and Tables | ||
|
( http://convert.french-property.co.uk ) |
||
| Cubic Centimeters (cm^3) To Cubic Meters (m^3) Conversion | ||
|
( http://www.asknumbers.com/CubicCentimeterToCubicMeter.aspx ) |
||
| Conversion of Metric and Imperial Units | ||
|
( http://www.imperialtometric.com/conversion_en.htm#volume ) |
||
| Volume Calculator | ||
|
( http://www.csgnetwork.com/volumecalc.html ) |
||
|
Section 7.5, p. 151, question 13 |
||
| Platonic Solids | ||
|
( http://whistleralley.com/polyhedra/platonic.htm. ) |
||
| Platonic Solids | ||
|
( http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_128_g_4_t_3.html?open=instructions&from=category_g... ) |
||